Automating RAG Deployment with OpenShift AI and Validated Patterns
Creating demos that are easily reproduced is key for collaboration and knowledge sharing. This blog post covers the steps followed to create automations, in a GitOps fashion, to deploy a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) demo on top of OpenShift, including the OpenShift AI infrastructure and its dependencies.
Why Validated Patterns?
We have opted for using the Validated Patterns framework. This represents an evolution of how applications are deployed in hybrid cloud environments. Validated Patterns automatically deploy a full application stack using a GitOps-based framework, including all necessary components and operators. This approach helps create business-centric solutions while maintaining Continuous Integration (CI) practices over your applications.
Deploying and configuring all the components for a RAG application, though not inherently difficult, can be tedious and error-prone. That’s why we created a validated pattern to automate the deployment of both the RAG components and the required infrastructure on top of OpenShift, particularly OpenShift AI and its dependencies.
OpenShift AI Validated Pattern
The RAG Demo Validated Pattern automates the installation and configuration of all components necessary for running OpenShift AI. This pattern significantly simplifies the deployment process, allowing you to deploy the RAG demo on OpenShift AI without manual intervention for each component.
The code for the validated pattern is located at https://github.com/luis5tb/rhoai-patterns-demo, and it is named rhoai-pattern-demo
Dependencies Installation
The rhoai-pattern-demo pattern handles the installation of several critical dependencies required to run AI workloads efficiently on OpenShift AI. These include:
-
OpenShift Serverless: Provides event-driven architecture, enabling applications to scale based on demand, without the need for constant resource allocation. This is required by the KServe component, used by OpenShift AI to deploy models.
-
OpenShift Service Mesh: Facilitates secure, reliable communication between microservices by providing routing, observability, and tracing. Again, this is used by the KServe component in OpenShift AI to deploy models.
-
OpenShift Authorino: Manages authentication and authorization policies, ensuring secure access to APIs and microservices. OpenShift AI leverages this to provide secure access to deployed models.
-
Node Feature Discovery (NFD) Operator: Detects hardware features on nodes, ensuring that resources such as GPUs are properly detected.
-
NVIDIA GPU Operator: Manages the provisioning and lifecycle of NVIDIA GPUs in OpenShift, allowing the OpenShift AI models and workbenches to leverage GPU acceleration for intensive AI computations.
By automating the installation and configuration of these components, the pattern ensures a smooth deployment of OpenShift AI, setting up the foundation for the RAG demo.
The pattern also handles the installation of the OpenShift AI Operator, responsible for managing the deployment and lifecycle of AI workloads on OpenShift AI. This operator simplifies the deployment and management of AI models, making it easier to deploy and manage AI applications on OpenShift AI.
All these operators are installed by adding their respective subscriptions into the subscription section in values-hub.yaml:
subscriptions:
serverless:
name: serverless-operator
namespace: openshift-serverless
channel: stable
servicemesh:
name: servicemeshoperator
namespace: openshift-operators
channel: stable
nfd:
name: nfd
namespace: openshift-nfd
channel: stable
nvidia:
name: gpu-operator-certified
namespace: nvidia-gpu-operator
channel: v24.6
source: certified-operators
authorino:
name: authorino-operator
namespace: openshift-operators
channel: tech-preview-v1
source: redhat-operators
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
rhoai:
name: rhods-operator
namespace: redhat-ods-operator
channel: alpha
source: redhat-operators
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
Additionally, the required namespaces with the proper configuration are specified in the same file:
namespaces:
- openshift-serverless:
operatorGroup: true
targetNamespaces: []
- openshift-nfd
- nvidia-gpu-operator
- redhat-ods-operator:
operatorGroup: true
targetNamespaces: []
Finally, to complete the installation process, some Custom Resources (CRs) need to be created so that the respective operators install the required components. The creation of these CRs is managed by adding the following to the values-hub.yaml file as applications, all of them part of a project in ArgoCD named openshift-ai:
projects:
- openshift-ai
applications:
nfd-config:
name: nfd-config
namespace: openshift-nfd
project: openshift-ai
path: charts/all/nfd-config
nvidia-config:
name: nvidia-config
namespace: nvidia-gpu-operator
project: openshift-ai
path: charts/all/nvidia-config
rhoai-config:
name: rhoai-config
namespace: redhat-ods-operator
project: openshift-ai
path: charts/all/rhoai-config
The charts path contains the yaml template used to create these CRs.
RAG Deployment with OpenShift AI
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique that combines traditional retrieval-based methods with generative models like large language models (LLMs). The key idea behind RAG is to retrieve relevant context (documents or data) from a database or external source, which is then used by the LLM to generate more accurate and relevant responses. This approach enhances the quality and relevance of generated outputs, making it highly useful for applications like intelligent search, customer support, and knowledge management.
The RAG-base demo assumes there is some private local data that needs to be used in conjunction with public data. This set of data needs to be added (at different times) to the VectorDB for retrieval and use as context for the LLM.
Once the OpenShift AI cluster setup is automated, we can proceed with the automation of the RAG components needed by our demo:
- VectorDB: In this case, ChromaDB.
- LLM: Either local or remotely deployed. In this demo, we use a remotely deployed LLM to save local resources.
- Pipelines: To initialize the VectorDB with base knowledge.
- Pipeline: To add extra data to the VectorDB depending on the question asked.
RAG automation
The code for this automation is available in the same repository but under the rag-demo branch: https://github.com/luis5tb/rhoai-patterns-demo/tree/rag-demo.
The automation process involves the following steps:
-
Utilize the default secrets management that comes from the template. To enable this, the
vaultandgolang-external-secretsapplications need to be added to thevalues-hub.yamlin their own project (hub):namespaces: - vault - golang-external-secrets projects: - hub applications: vault: name: vault namespace: vault project: hub chart: hashicorp-vault chartVersion: 0.1.* golang-external-secrets: name: golang-external-secrets namespace: golang-external-secrets project: hub chart: golang-external-secrets chartVersion: 0.1.*Then add your keys to the `values-secret.yaml.template, for example:
secrets: - name: config-demo vaultPrefixes: - global fields: - name: secret onMissingValue: generate vaultPolicy: validatedPatternDefaultPolicy - name: minio-secret fields: - name: minio_root_user value: MY_MINIO_USER - name: minio_root_password value: MY_MINIO_PASSWORD - name: openai-keys fields: - name: OPENAI_API_BASE value: MY_OPENAI_API_BASE - name: OPENAI_API_KEY value: MY_OPENAI_API_KEY -
Automate the setup of S3 storage for private documents. In this demo, for simplicity, it is also used for public documents. The S3 storage setup is done using MinIO as it is simple to deploy. This automation includes deploying the MinIO application and creating an initial bucket for the documents:
clusterGroup: namespaces: - minio-ns projects: - s3 applications: minio: name: minio namespace: minio-ns project: s3 path: charts/all/minio vars: minio: bucket_name: localdocs -
Deployment of VectorDB, in this case, ChromaDB:
namespaces: - chromadb-ns projects: - vectordb applications: chromadb: name: chromadb namespace: chromadb-ns project: vectordb path: charts/all/chromadb -
Automate OpenShift AI resources, including the Data Science project (a namespace with extra annotations/labels), the Pipeline server inside it, and the secret with credentials to access the LLM endpoint:
namespaces: - rag-demo: annotations: openshift.io/description: 'RAG Workspace' openshift.io/display-name: 'RAG Workspace' labels: kubernetes.io/metadata.name: "rag-demo" modelmesh-enabled: 'false' opendatahub.io/dashboard: 'true' projects: - rag applications: rag-demo: name: rag-demo namespace: rag-demo project: rag path: charts/all/rag
Steps to Deploy RAG on OpenShift AI
With the dependencies in place, deploying the RAG demo on OpenShift AI can be done in a few automated steps:
-
Clone the Validated Pattern Git repository: The pattern repository contains the automation scripts and GitOps configuration files.
-
Apply the GitOps manifests: Using OpenShift GitOps, apply the manifests to trigger the deployment of all necessary components. This is done by configuring your secrets in
values-secret.yaml.templateand copying them to your config folder (e.g.,~/.config/hybrid-cloud-patterns/values-secret-rhoai-pattern-demo.yaml), and then triggering the installation:$ cp values-secret.yaml.template ~/.config/hybrid-cloud-patterns/values-secret-rhoai-pattern-demo.yaml $ ./pattern.sh make install -
Configure the RAG pipelines: After the infrastructure is in place, the OpenShift AI project is created, and the pipeline server is configured. You can import the required pipelines and upload the necessary documents to the MinIO buckets. This last step is not automated yet:
-
Add documents to the appropriate folder in the Minio
localdocsbucket: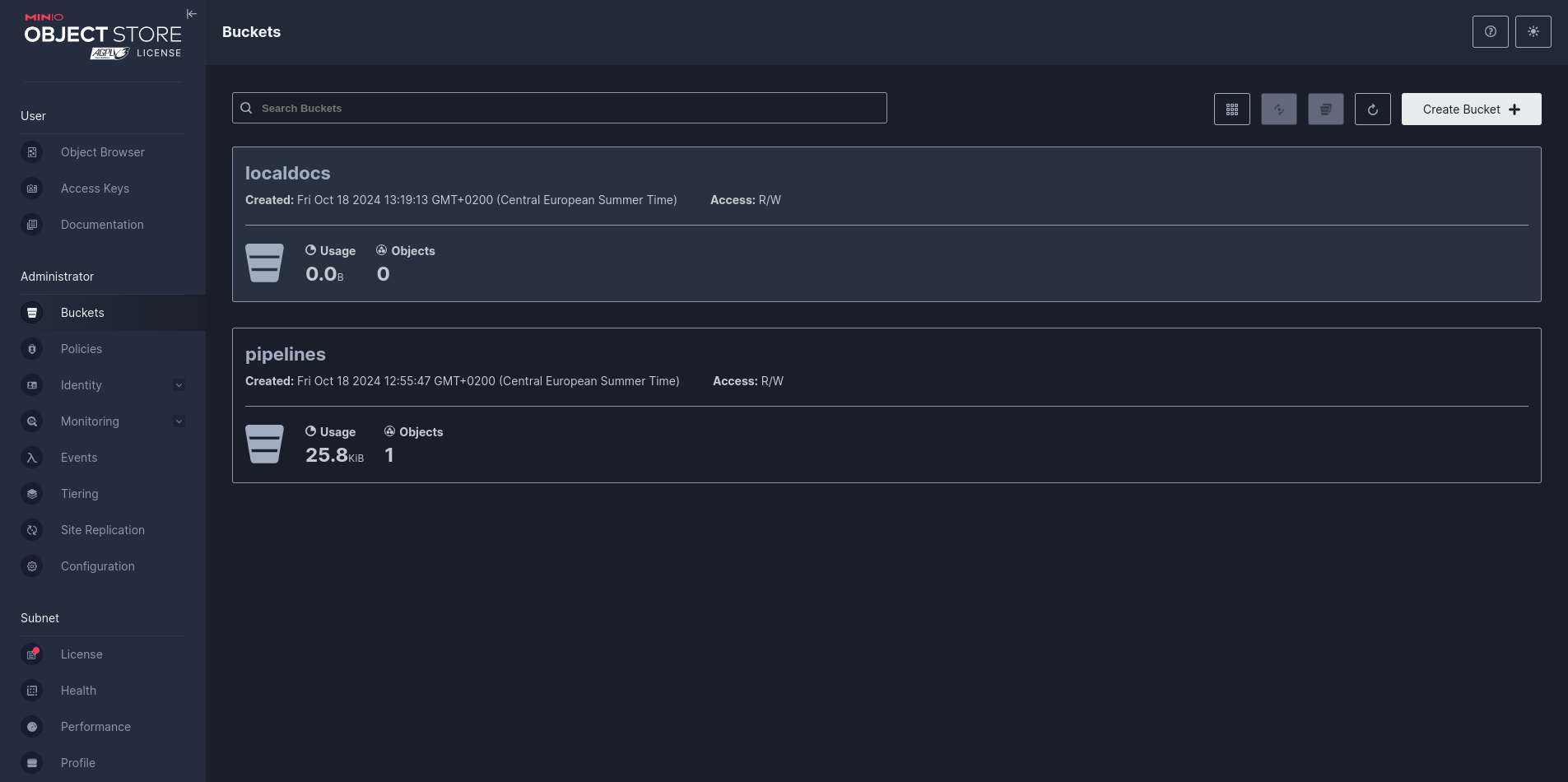
You can retrieve the Minio UI endpoint from the OpenShift developer console:
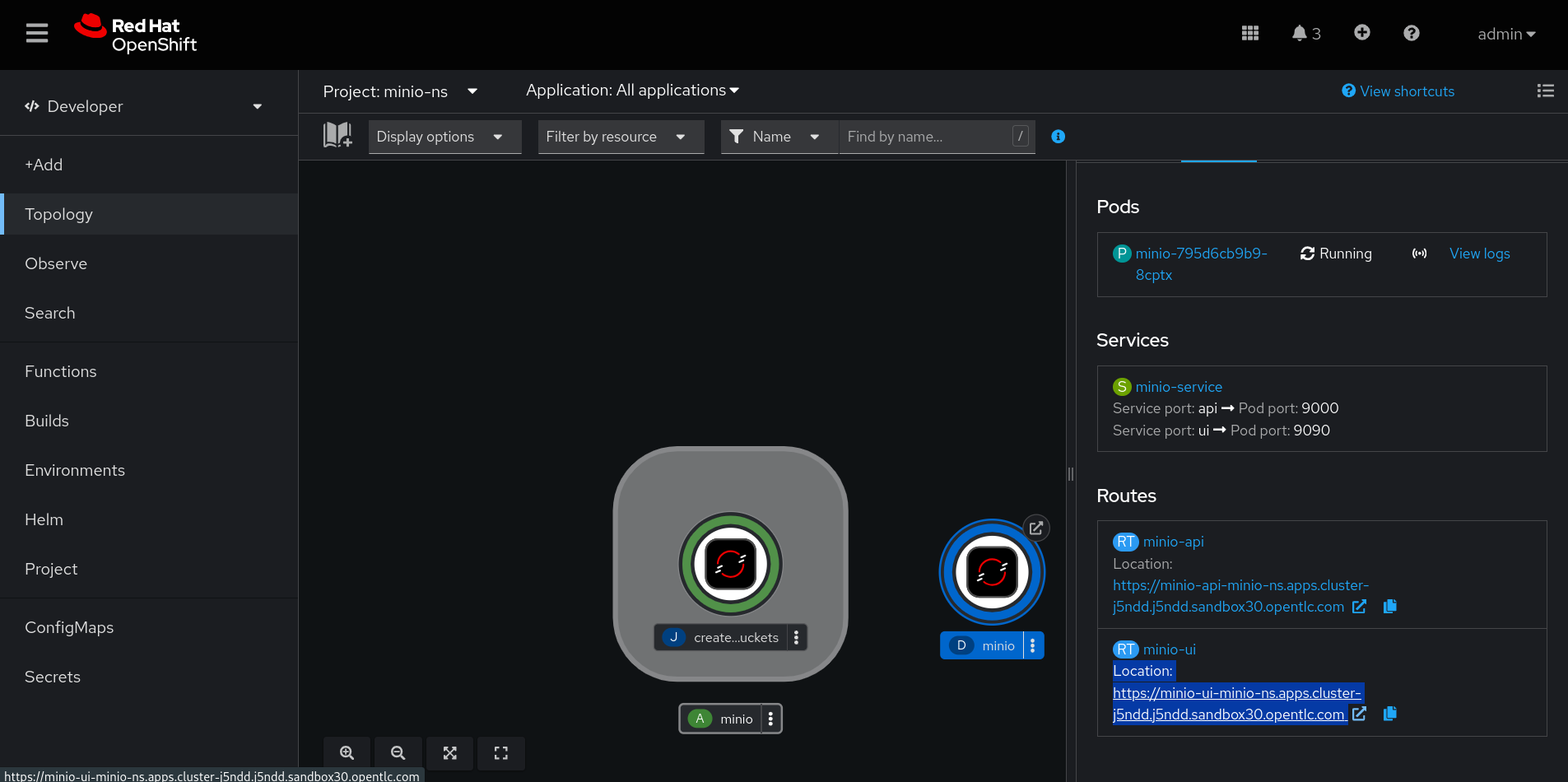
-
Import the VectorDB initialization pipeline. A sample is available at:
https://github.com/luis5tb/rhoai-patterns-demo/tree/rag-demo/sample_pipelines/initialize_vectordb_pipeline.yaml:
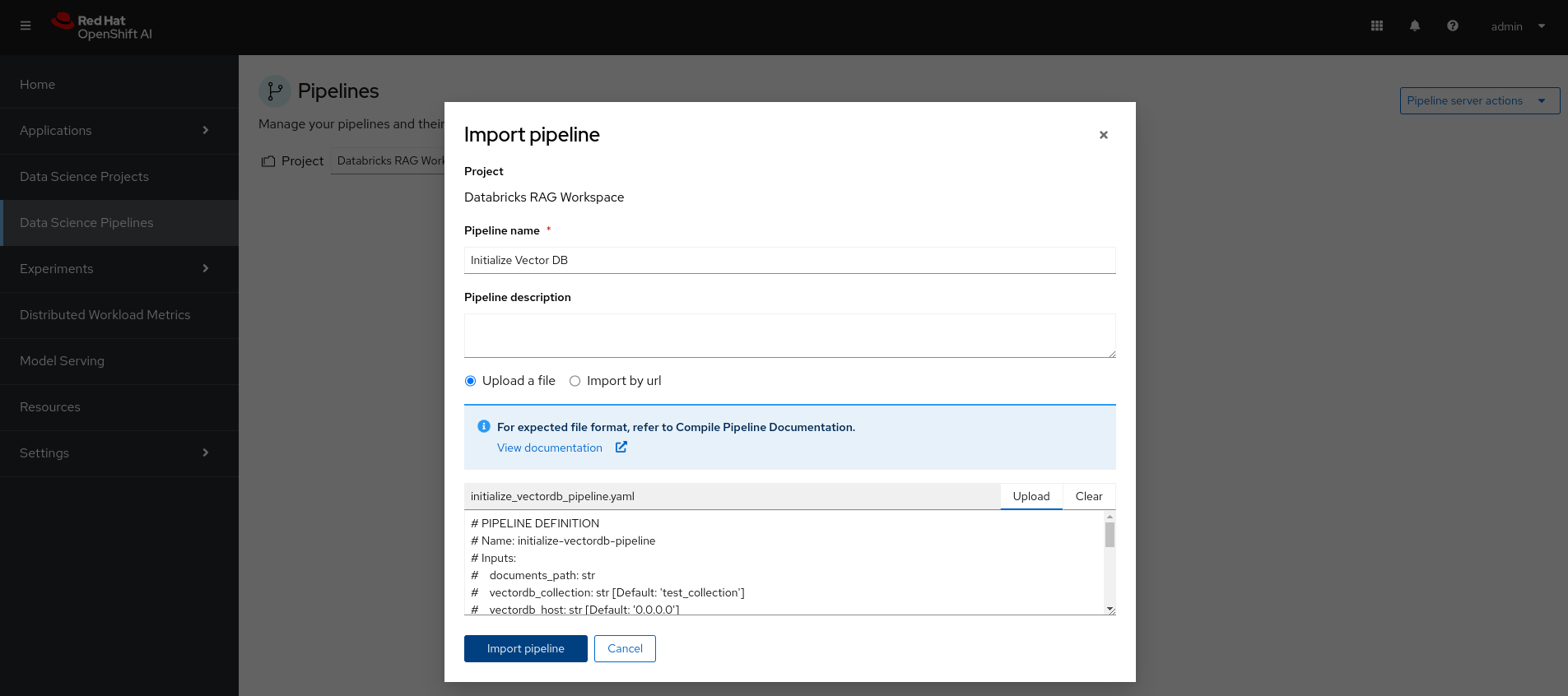

-
Trigger the pipeline. You will need the VectorDB (internal) endpoint, which you can get from the OpenShift console:
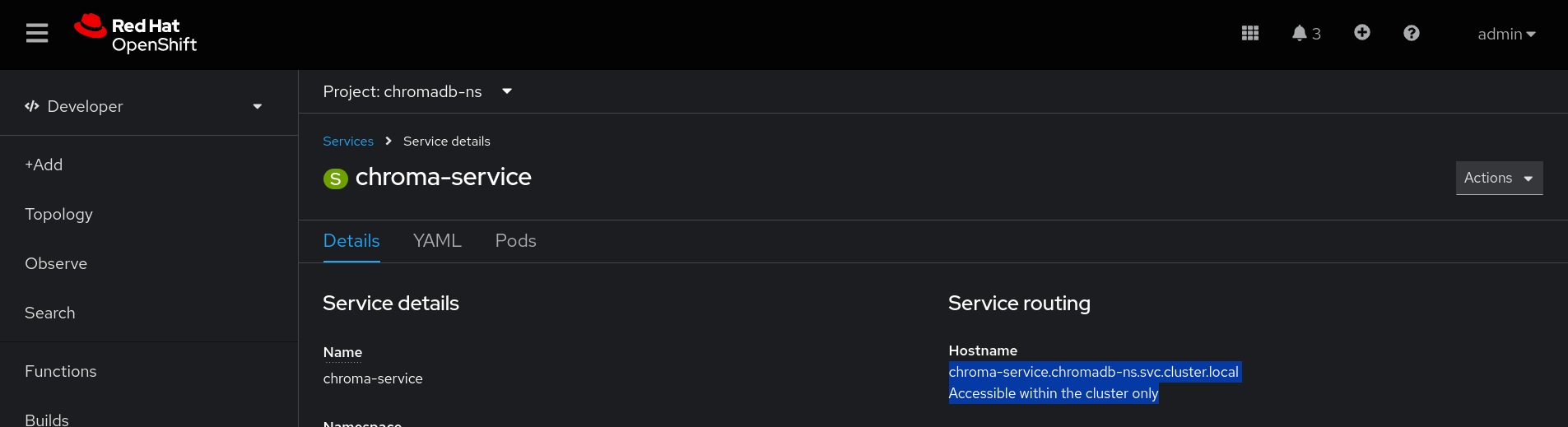
-
Import the RAG pipeline. A sample is available at:
https://github.com/luis5tb/rhoai-patterns-demo/tree/rag-demo/sample_pipelines/rag_pipeline.yaml: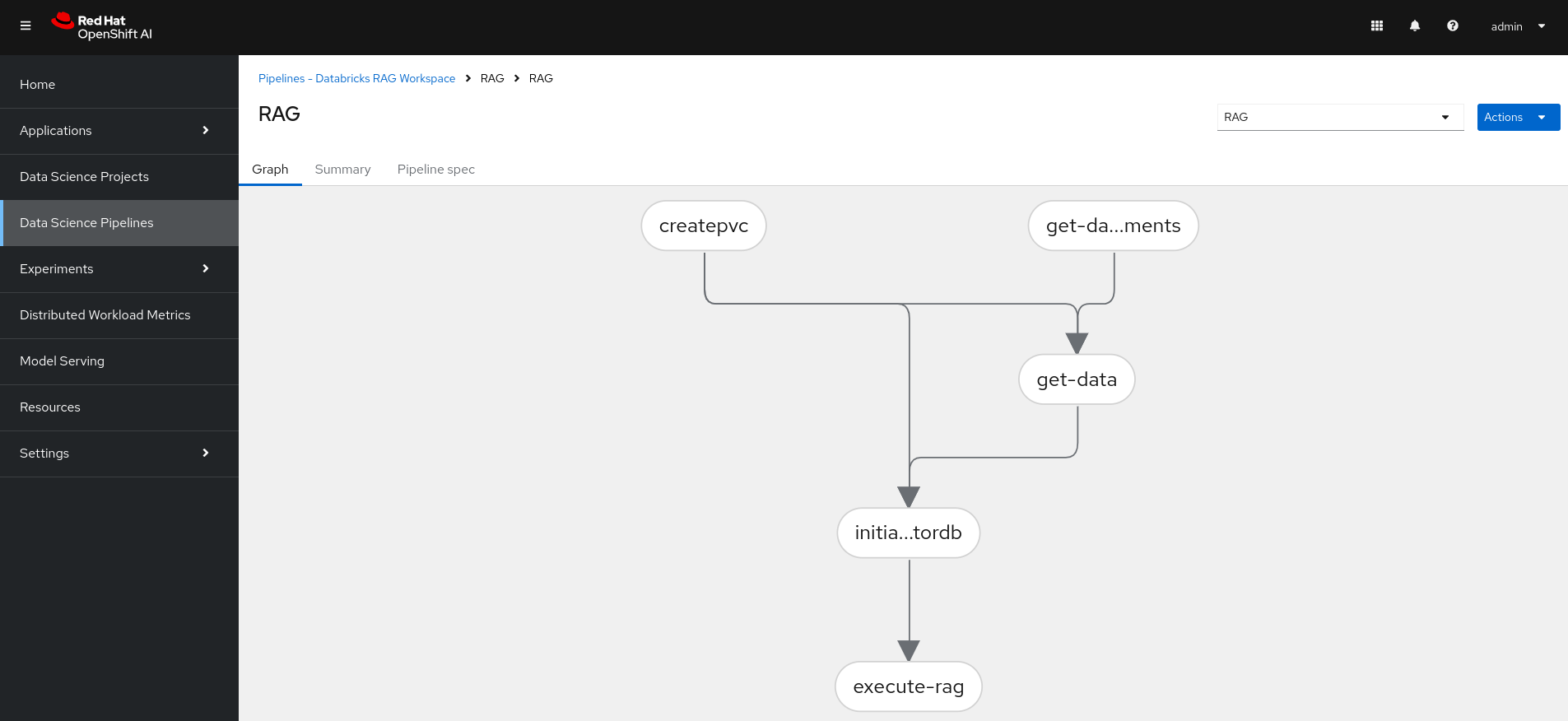
-
Trigger the RAG pipeline. Fill in the required values (including the ChromaDB endpoint from earlier) and the question you wish to answer.
-
Conclusions
The rhoai-pattern-demo Validated Pattern simplifies and automates the deployment of a RAG application, leveraging a GitOps-based approach to ensure consistency and repeatability. By using this pattern, you can focus on building and refining your AI applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure and configuration, reducing errors and saving time.
With the increasing complexity of AI workloads and hybrid cloud environments, validated patterns offer a streamlined way to deploy business-critical applications efficiently. Whether you’re experimenting with RAG or building production-ready AI solutions, this automation accelerates your workflow on OpenShift.